Introduction
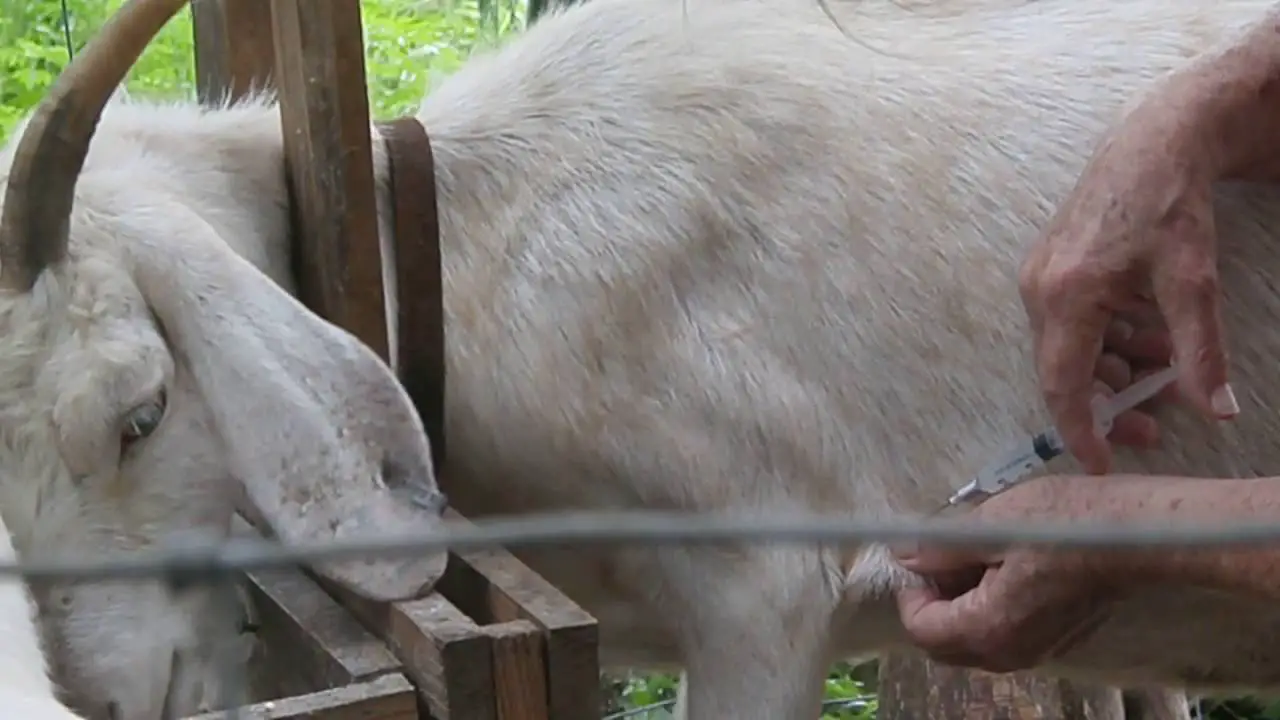
Proper vaccination plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of goats. Vaccines help protect goats from various diseases, ensuring their longevity and productivity. In this article, we will discuss the recommended vaccines for goats, the age at which they are administered, and the specific diseases they help prevent.
Table of contents
Clostridial Vaccines
Clostridial diseases are a significant concern for goat owners, as they can be fatal if left untreated. The following clostridial vaccines are commonly administered to goats:
- Clostridium perfringens Types C and D Antitoxin: Administered to newborn kids within the first 24 hours of life, this vaccine provides passive immunity against Clostridium perfringens types C and D toxins, which cause enterotoxemia.
- Clostridium perfringens Types C and D Vaccine: At four to six weeks of age, kids should receive their first dose of this vaccine, followed by a booster shot four weeks later. This vaccine helps protect against enterotoxemia, a condition characterized by severe diarrhea and enteritis.
- Tetanus Antitoxin: Given to newborn kids within the first 24 hours of life, this vaccine provides passive immunity against tetanus, a bacterial disease caused by Clostridium tetani.
- Tetanus Toxoid: At four to six weeks of age, kids should receive their first dose of tetanus toxoid, followed by a booster shot four weeks later. Tetanus toxoid provides active immunity against tetanus.
Caprine Arthritis and Encephalitis (CAE) Vaccine
CAE is a viral disease that affects goats, causing arthritis, encephalitis, and mastitis. The CAE vaccine is recommended for all goats, and it is typically administered when kids reach two to four months of age. An initial dose is given, followed by a booster shot four to six weeks later. Annual revaccination is recommended to maintain immunity.
Caseous Lymphadenitis (CL) Vaccine
Caseous lymphadenitis is a chronic bacterial disease in goats that leads to abscesses in lymph nodes. Vaccination can help control the spread of this highly contagious disease. The CL vaccine should be given to kids at three months of age, with a second dose four weeks later. Annual revaccination is essential to ensure continued protection.
Leptospirosis Vaccine
Leptospirosis is a bacterial disease that can affect both goats and humans. The leptospirosis vaccine is recommended for goats in regions where the disease is prevalent or as advised by a veterinarian. The initial vaccination is typically given to kids at three to four months of age, followed by a booster shot four weeks later. Annual revaccination is necessary to maintain immunity.
Goat Rabies Vaccine
Rabies is a deadly viral disease that can affect all mammals, including goats. While rabies is less commonly seen in goats compared to other species, it is essential to consider vaccination if your goats are at risk due to geographic location or potential exposure to wildlife. The goat rabies vaccine provides crucial protection against this fatal disease.
The administration of the goat rabies vaccine may vary depending on regional regulations and veterinarian recommendations. It is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate vaccination protocol for your goats. In general, the following guidelines can be considered:
- Age of Vaccination: The initial rabies vaccine is typically given to goats at three to four months of age. However, regional regulations and veterinarian guidance may vary, so consult with a professional to determine the specific age for vaccination.
- Booster Shots: After the initial vaccine, goats will require regular booster shots to maintain immunity. The timing and frequency of booster shots may vary depending on local regulations and the specific vaccine used. Typically, annual revaccination is recommended to ensure continuous protection against rabies.
- Monitoring and Prevention: In addition to vaccination, it is crucial to implement preventative measures to reduce the risk of exposure to rabies. This includes proper enclosure and fencing to prevent contact with wildlife and regular monitoring for any signs of abnormal behavior or illness in your goats.
Remember that rabies is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. Vaccinating your goats not only protects their health but also reduces the risk of transmission to yourself, other animals, and your community.
Conclusion
Vaccinating goats is an essential aspect of their overall health management. By following the recommended vaccination schedule, goat owners can protect their animals from various diseases and ensure their long-term well-being. Remember to consult with a veterinarian for specific guidance on vaccine selection, timing, and any regional disease risks. By prioritizing vaccination, you are taking proactive steps to safeguard the health and productivity of your goat herd.




