In this guide to goat illnesses and symptoms, we describe some of the illnesses that you may encounter in your goats. If you’re a new farmer, you should be aware of these problems so you can be be aware of what can go wrong with your goats.
It is good practice to regularly inspect your goats for signs of illness. Also monitor their behavior. When something does not seem right, consult with your veterinarian.
Do not administer medicine or begin treatment until you have consulted with your trusted veterinarian.
Table of contents
- Goat Polio
- Enterotoxemia in Goats
- CAE in Goats
- Coccidiosis in Goats
- Goat Bloat
- CL in Goats
- Copper Deficiency in Goats
- Tetanus in Goats
- Pneumonia in Goats
- Contagious Caprine Plueropneumonia in Goats
- Floppy Kid Syndrome in Goats
- Weak Kid Syndrome
- Goat Mastitis
- Goat Ketosis (Pregnancy Toxemia in Goats)
- Copper Toxicity in Goats
- Thiamine Deficiency in Goats
- Tapeworms in Goats
- Paratuberculosis in Goats (Johne’s Disease in Goats)
- Video: Carolina Kiko Classic – Johne’s Disease in Goats
- Listeriosis in Goats
- Photo Credits
Goat Polio
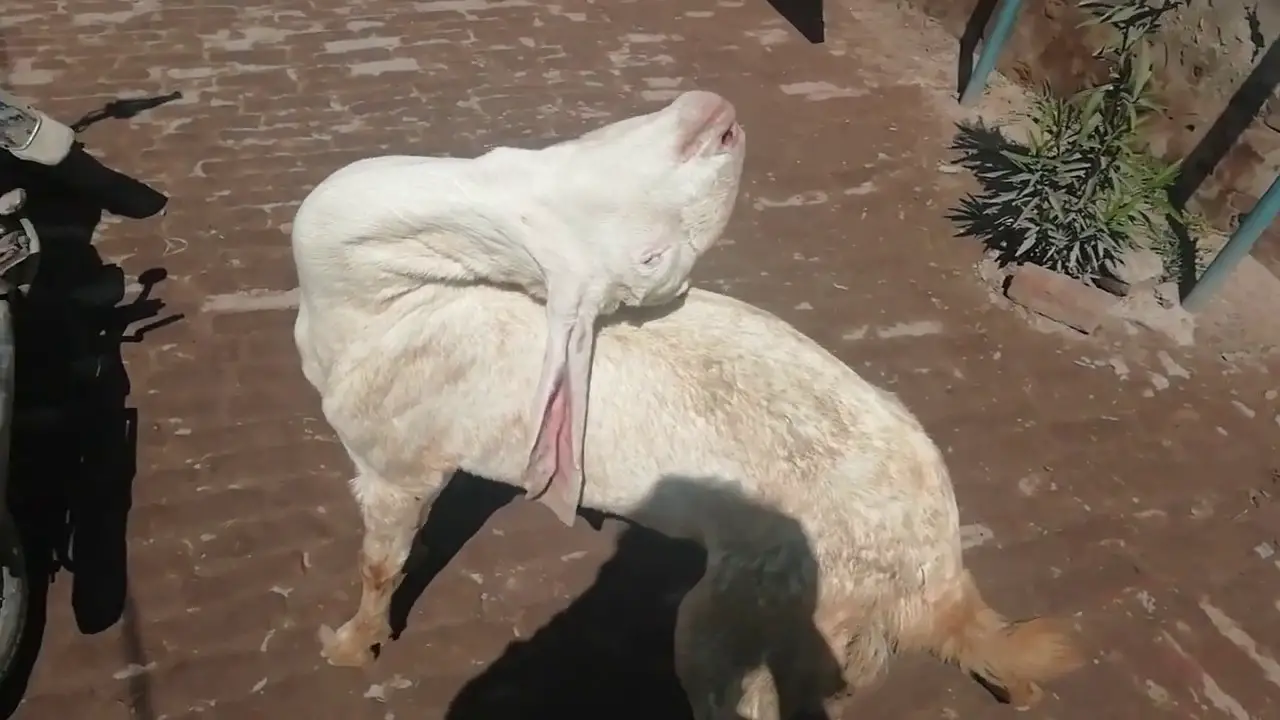
Goat polio, also known as polioencephalomalacia (PEM), is a neurological disorder that affects goats. It is caused by a deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1) and /or sulfur toxicity. PEM can lead to symptoms such as seizures, blindness, and uncoordinated movements, including tremors and convulsions. Other symptoms of goat polio can include teeth grinding, head pressing (pushing its head against a wall), increased aggression, rapid involuntary movement of the eyeballs (called nystagmus) and opisthotonos, which is a muscle spasm that causes the goat to severely arch its back and throw its head backwards in an abnormal position. See the photo below.
Goats produce thiamine in their rumen (stomach) via the microbes that live there. Disruption of the amount of B1 available to the goat can occur in two ways. Either not enough thiamine gets made or there are too many thiaminases, which are enzymes that break down the thiamine.
Goat Polio occurs after a change of food, or anything that causes a disruption to the microbes. This can occur if there is not enough roughage in the diet, too much grain in the diet, feeding on a newly fertilized field, eating chicken feed or from grain bins, or eating too much fruit that has fallen from a tree. Polio in Goats can also occur from dehydration, sulfur poisoning, lead poisoning, moldy hay, or as a side effect of medications. In North America, the disease is seen more frequently in the winter, when farmers rely more on grain feeding.
Goat polio can be prevented by providing a balanced diet that contains adequate levels of grasses and hay. If a goat is suspected of having goat polio, it is important to consult a veterinarian. The veterinarian can diagnose the condition and provide appropriate treatment, which may include administering thiamine supplements and modifying the goat’s diet. In severe cases, the goat may require hospitalization and supportive care, or it may perish.
Treatment of polio in goats should be initiated as soon as possible to prevent permanent damage to the goat’s nervous system. Early detection and proper treatment can help improve the goat’s chances of making a full recovery. If treatment does not occur quickly, the goat will usually die within 1 to 3 days.

Enterotoxemia in Goats
Enterotoxemia in goats is another illness that occurs when the digestive system of goats gets out of balance. It also known as overeating disease or pulpy kidney disease, and it is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium perfringens type C and D. These bacteria are present in healthy animals, but in small numbers. Enterotoxemia in goats is a potentially fatal condition that can occur when goats consume large amounts of rapidly fermentable carbohydrates, such as those found in high-carbohydrate forages, grains, milk, protein supplements, or milk replacers (in the case of kids). The rapid fermentation leads to an overgrowth of the Clostridium perfringens bacteria in the goat’s rumen, which produces toxic substances that can enter the bloodstream and cause systemic illness. The toxins spread rapidly to the brain and can cause death within minutes or hours.
Common symptoms of enterotoxemia in goats include sudden death, bloating, depression, lethargy, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. In severe cases, the goat may also experience abdominal pain, rapid heartbeat, lethargic behavior, and convulsions. The goat may kick at its abdomen, repeatedly lay down and stand up, lay on its side, or cry out.
Prevention has a better outcome than treatment. Goats should also be vaccinated against enterotoxemia with the CD&T vaccine. Check with your veterinarian. Additionally, it is important to manage the goat’s diet carefully, avoiding large amounts of grains and other high-carbohydrate feed. Farmers should implement good management practices, such as keeping feed and water containers clean, to reduce the risk of bacterial contamination.
If enterotoxemia is suspected, it is important to seek veterinary care immediately, as the disease can progress quickly and can be fatal if left untreated. Treatment typically involves administering antibiotics and providing supportive care, such as fluid therapy and nutritional support, to help the goat recover. Early detection and treatment are critical to improving the goat’s chances of survival.

CAE in Goats
Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis (CAE) is a viral disease that affects goats. It is caused by a type of virus called and lentivirus, specifically the Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis virus (CAEV). (This is a type of small ruminant lentivirus, which is also known as SRLV.) The disease is characterized by inflammation of joints (arthritis) in adults goats and encephalitis, which is inflammation of the the brain and brain stem, in kids under 4 months old.
CAE is a chronic disease that is often asymptomatic in the early stages in adults, but as the virus spreads and damages the joints, it can cause swelling, pain, and lameness. Goats may walk on their knees and refuse to stand up. Joints become swollen, the goats lose weight, and their coat is impacted. Goats may push their head into a wall or fence, a behavior known as head pressing.
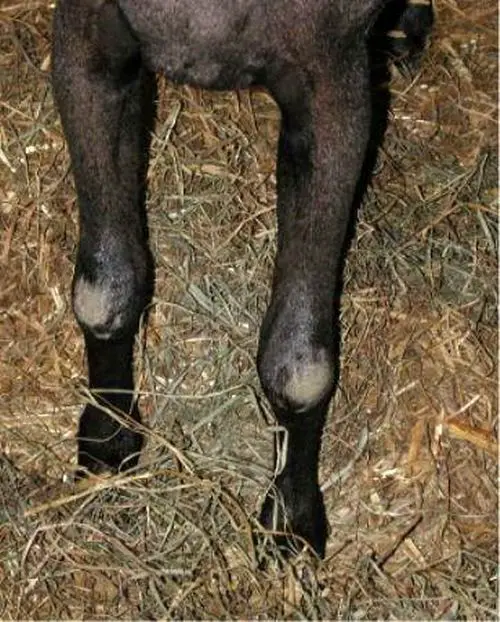
CAE is typically spread from mother to kid through milk and colostrum. It may also spread among goats via contaminated bodily fluids such as semen, feces, and urine; or through contaminated equipment such as milking machines or tattooing and vaccinating equipment that is used on multiple animals.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for CAE. Steps can be taken to manage the disease, however, including providing affected goats with a comfortable environment and minimizing stress, as well as limiting the spread of the virus to other animals through careful management practices.
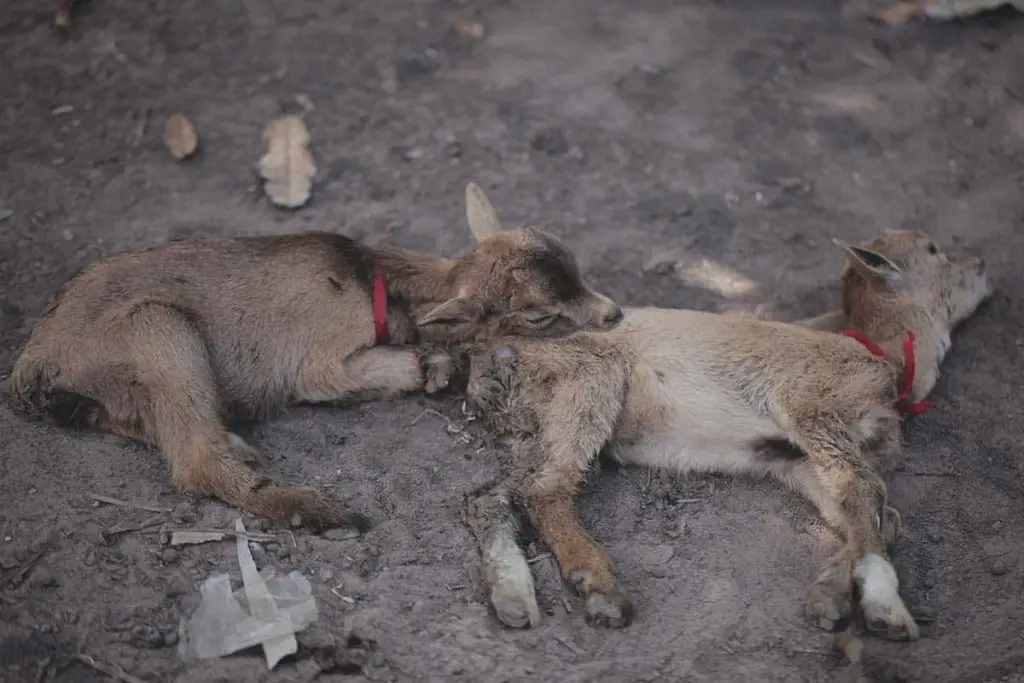

Kids ages two to four months old are most likely to contract the CAE virus, encephalitis form. The kids become paralyzed, which may be followed by seizures and sometimes death.
There is not a vaccine for CAE of SRLV. It is important for goat owners to have their animals tested for CAE to prevent its spread and to implement management strategies to minimize the impact of the disease on their herd.

Coccidiosis in Goats
Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease that affects the intestinal tract of various animals, including chickens, turkeys, cattle, sheep, and goats. It is caused by the protozoan parasite (coccidia) Eimeria and is characterized by symptoms such as diarrhea, weight loss, dehydration, and decreased feed efficiency.
Almost all goats have some level of Eimeria in their guts. Problems occur when a large quantity of the protozoa are introduced at one time, and young kids and kids who have just been weaned are the most susceptible. Transmission occurs through contaminated feed or water. The protozoa create oocysts, which damage the lining of the goat’s intestines. The oocysts produce thousands of oocytes which are released into the environment in fecal matter. The oocytes can remain viable in dark, warm, and moist environments, and once ingested by another goat, the cycle begins again. You can see how this can be a common health problem in goats.
Treatment for coccidiosis typically involves the use of antiparasitic drugs, such as sulfonamides or coccidiostats, which are added to the feed or water. Contact your veterinarian and the first signs of infection. Prevention of the disease can be achieved through good management practices, such as maintaining clean and dry living areas, proper sanitation, and the use of proper feed and water.
In addition to treating and preventing coccidiosis in individual animals, it is important to implement control measures at the herd level to minimize the spread of the parasite and reduce the overall impact of the disease. Goat housing should be kept dry and have adequate exposure to sunlight. Direct sunlight and freezing temperatures kill most oocytes.
Note that coccidia Eimeria are host specific. This means that the species of Eimeria that infect goats can only infect goats, and species that infect other animals do not infect goats. (There are at least 1700 different species, but only about 12 infect goats.)

Goat Bloat
Bloat is a condition in which the goat’s rumen becomes enlarged and filled with gas. It can cause the goat to become bloated, have difficulty breathing, and become distressed.
Please check out our thorough stand alone article on goat bloat.
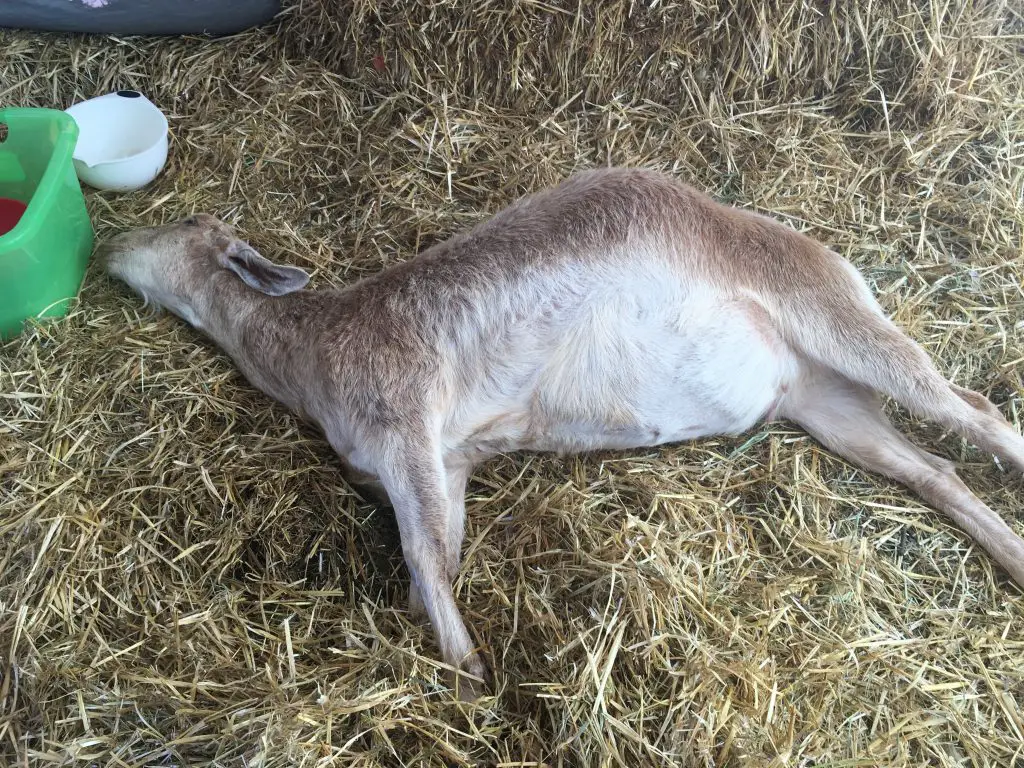

CL in Goats
Caseous Lymphadenitis is a bacterial infection that affects the lymph nodes of goats. It can cause abscesses and swelling in the affected area and can lead to chronic infections and spreading of the disease to other animals.
Please check out our thorough stand alone article on Caseous Lymphadentis.
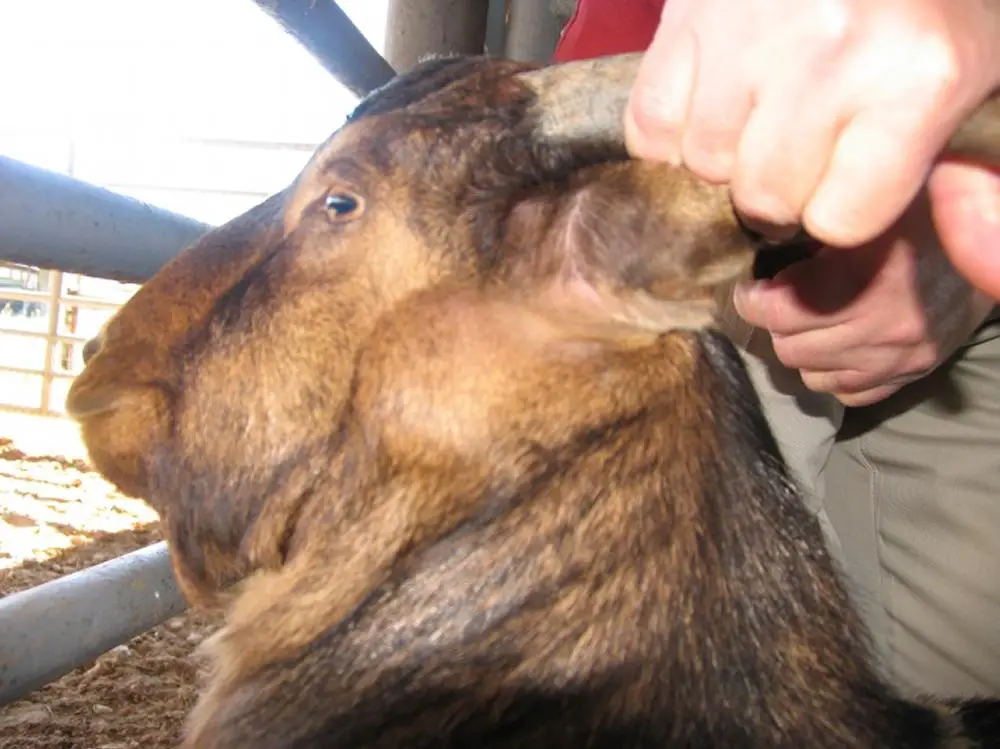
Copper Deficiency in Goats
Copper deficiency is a common nutritional problem in goats and can result in various health problems, including anemia, reduced growth rate, reproductive problems, and an increased susceptibility to infections. Copper is an essential mineral that is involved in a number of physiological processes, including the formation of red blood cells, the maintenance of a healthy immune system, hair pigmentation, and the production of collagen, which is necessary for the proper functioning of bones, tendons, and ligaments.
In goats, copper deficiency can occur due to a number of factors, including a diet that is low in copper, an excess of other minerals that interfere with copper absorption, or a being born to a doe that had inadequate dietary copper. Copper deficiency is often seen not only in regions with soil that is naturally low in copper (such as Australia) but also in regions with high levels molybdenum and sulfur – even if the copper level is normal. It can also be a problem in areas where goats are fed predominantly grain-based diets, and over supplemented with minerals (they can contain high levels of molybdenum, sulfur, or iron).
The diagnosis of copper deficiency in goats is typically based on clinical signs, such as anemia and changes in the color of the coat, as well as on blood tests that measure copper levels. Treatment of copper deficiency involves supplementation with copper in the form of copper sulfate or another copper supplement, either in the feed or by injection.
For kids born with copper deficiency, however, the prognosis is grim. Kids can look normal when they are born, but develop swayback after 4-6 weeks. This means that their hind limbs are uncoordinated, and they develop an erratic, unsteady gait. The hind limbs may become paralyzed. Once these signs occur in kids, they are permanent and typically get worse. Copper supplements for kids will not reverse the symptoms.
Supplementing goats with too much copper can also be a problem, however, because copper poisoning can occur. Check with your veterinarian before engaging in any mineral supplementation.
Prevention of copper deficiency in goats can be achieved through proper nutrition and the use of balanced rations that contain adequate levels of copper. It is also important to avoid over-supplementation of other minerals, such as iron and molybdenum, which can interfere with copper absorption. Regular monitoring of copper levels in the herd is recommended to detect and address deficiency before it leads to more serious health problems.
Tetanus in Goats
Tetanus in goats is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani, which produces a potent neurotoxin (toxin that affects the nervous system). In goats, tetanus can occur when the bacterium enters the body through wounds, such as cuts or puncture wounds, and produces toxins that cause muscle stiffness and spasms.
The symptoms of tetanus in goats can vary, but typically include stiffness and spasms in the jaw muscles (lockjaw), which can make it difficult for the goat to eat and drink. Other symptoms can include muscle stiffness and spasms in the legs, tail, and neck, as well as a rigid, arched neck and an exaggerated extension of the legs. In severe cases, tetanus can lead to convulsions and death. If the diaphragm muscles are paralyzed, the goat will be unable to breathe, and will die.
Diagnosis of tetanus in goats is typically based on a combination of clinical signs and a history of recent wounds or injuries. Treatment of tetanus involves a combination of wound management, supportive care, and antibiotics to eliminate the bacterial infection. In addition, tetanus antitoxin may be administered to neutralize the toxins produced by the bacterium.
Prevention of tetanus in goats can be achieved through good wound management, including prompt and thorough cleaning of wounds and the use of proper wound care techniques. Inspect your herd for wounds that occur due to accidents, animal attacks, or fights. In addition, take good care of the wounds after ear tagging, castration (particularly if using elastrator bands), dehorning, and vaccinating. Furthermore, regular vaccination against tetanus can help reduce the risk of infection. It is important to consult a veterinarian if you suspect that your goat may have tetanus, as early and aggressive treatment is critical for the best outcome.
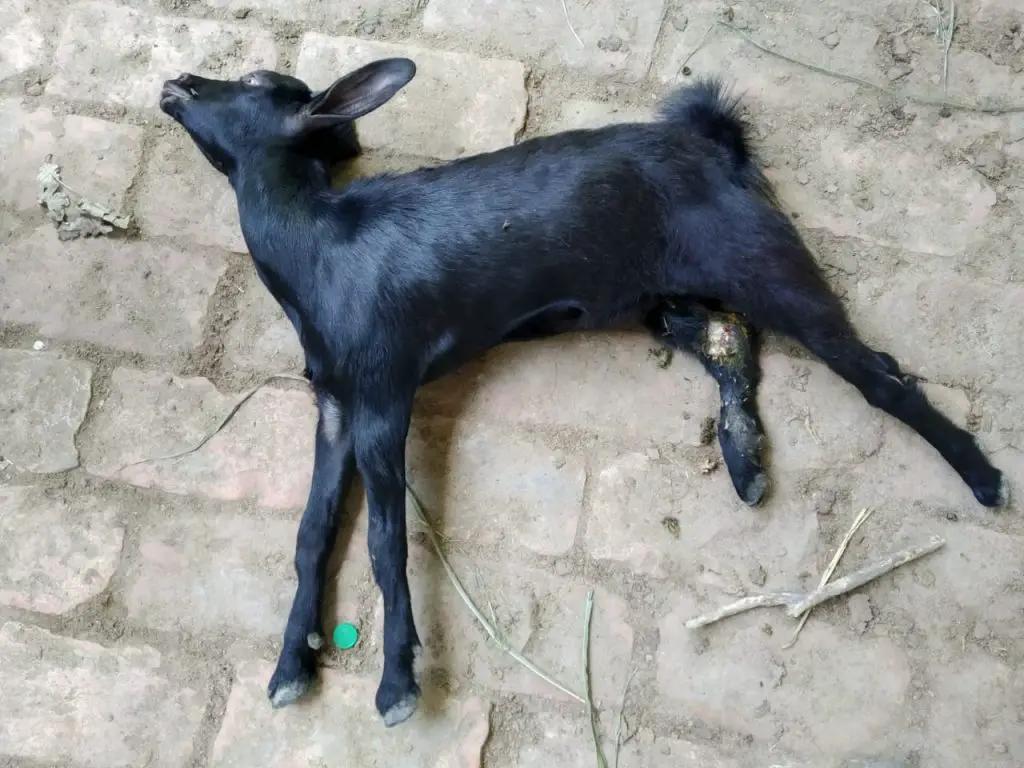

Pneumonia in Goats
Pneumonia is a common respiratory illness that affects goats and can be caused by a variety of agents, including bacteria, viruses, lungworm, and aspirations from incorrect drenching. Pneumonia in goats can range from mild to severe, and it can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Goats who are stressed are more susceptible to bacterial and viral pneumonia. The bacteria and viruses are are usually already present in healthy animals, but being stressed can lower the goat’s resistance, and enable the pathogens to multiply and cause illness.
The symptoms of pneumonia in goats can vary, but typically include coughing, nasal discharge, loss of appetite, and a fever. In severe cases, the goat may show signs of difficulty breathing, such as rapid breathing, grunting, or wheezing, and it may develop a bluish tint to the mucous membranes due to a lack of oxygen. The goats may have a high fever.
Bacterial pneumonia is often first detected after a necropsy is performed on an animal that has died suddenly. At that point, the other animals in the herd need to be examined carefully. Goats may not show obvious signs of distress, so it is important that you be aware of the animals’ typical behaviors. Take your goat’s temperature using a rectal thermometer to look for signs of inflammation.
Treatment of pneumonia in goats typically involves the use of broad spectrum antibiotics, and sometimes euthanasia. If the causes is suspected to be lungworm, then an anthelmintic drench is the proper course of action.
Prevention of pneumonia in goats can be achieved through good husbandry practices and preventing stress. Maintain a clean and dry living environment, and allow for adequate ventilation. Provide shelter for sudden temperature changes, and avoid overcrowding. It is also important to keep goats healthy through proper nutrition and plenty of fresh water. Stress is thought to be the biggest culprit, because it can weaken the immune system and make the goat more susceptible to respiratory infections. If you suspect that your goat has pneumonia, it is important to consult a veterinarian promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Contagious Caprine Plueropneumonia in Goats
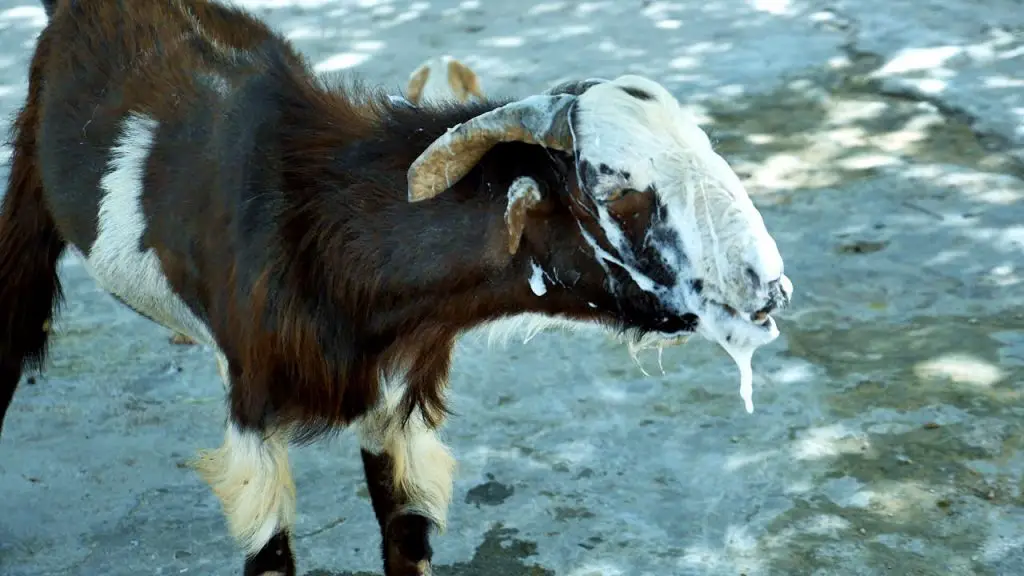
CCPP, or Contagious Caprine Pleuropneumonia is one of the most severe infections in goats. It is usually fatal. It is highly infectious, and it spreads by aerosol droplets. It is endemic in over 40 countries, but not in North America. It does not affect humans.
Signs of CCPP in goats are frothy nasal discharge, stringy saliva, high fever, coughing, difficulty breathing, lethargy, and not eating. If you suspect CCPP, contact your vet immediately.

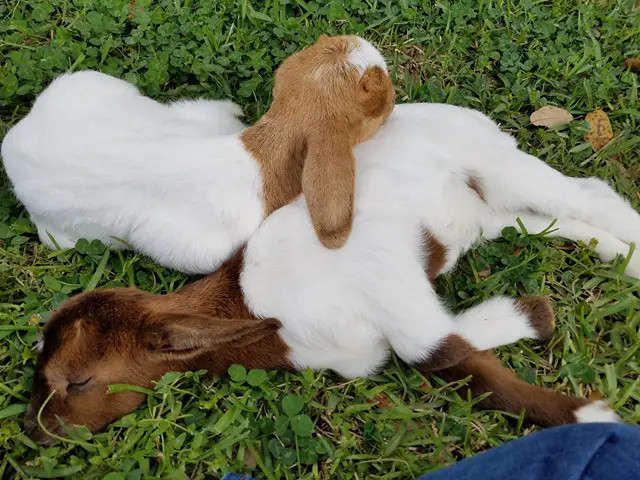
Floppy Kid Syndrome in Goats
Floppy Kid Syndrome is a condition that affects goats that are a few days old. It different than Weak Kid Syndrome, which is described in the next section.
The symptoms of Floppy kid syndrome are lack of muscle tone. This occurs in goats that were born normally and seem to thrive at first. Then between the 3rd and 10th day of their life, things change for the worse. The first symptom you may notice is that their tongue does not work to suckle, although they are able to swallow. They do not have diarrhea, nor other symptoms such as dehydration, labored breathing, or a swollen abdomen. When you pick up the kid you will notice that it is like picking up a rag doll. They are just floppy.
There are several diseases that can cause profound muscle weakness, and these need to be ruled out: Enterotoxaemia (Clostridial), Starvation, White muscle disease (Selenium/Vitamin E deficiency), Severe Bronchopneumonia, Sepeticaemia, Hypoglycemia, Colibacillosis, Abomasal bloat, Hypothermia, and Botulism. If all of these are ruled out, then the differential diagnosis is Floppy Kid Syndrome.
Floppy Kid Syndrome is the result of metabolic acidosis. This means that the blood of the kid has become acidic, and the goat will die without treatment. Get in touch with your veterinarian immediately. Your vet may recommend treatments with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) or antacid, and follow up with antibiotics.
What you don’t want to do is try to get the kid to eat more. While the exact causes are not known, It is strongly believed that overeating is at the root of the problem. Floppy Kid Syndrome occurs when the goat ingests milk more quickly than it can digest it. It is believed that the milk stays in its stomach too long, is not processed properly, and that causes the wrong microbes to multiply, leading the acidosis.
To prevent floppy kid syndrome, you need to be very careful if you are bottle feeding that you don’t overfeed the kid. Work with your vet to establish an appropriate routine. If the goats are suckling from nannies, then it is better if the nannies are in the pasture. When the kids are the nannies are in an enclosed pen, the kid can have too much access to food. This may be especially important if you have taken steps to fortify the nannies milk by giving the nannies supplements or concentrated feed or letting them feed in improved pastures before parturition (giving birth).

Weak Kid Syndrome
Weak kid syndrome starts at birth. It is different than Floppy Kid Syndrome, described above. Weak Kid syndrome results in a lack of coordination and weakness in the legs. The condition is most commonly seen in the first few days of life, and it can be caused by a number of factors, including hypothermia, malnutrition, lack of colostrum intake, and infections such as pneumonia or septicemia. It could also be caused by reduced food supply from the placenta while the kid was gestating, malnutrition in the dam or doe, disease in the mother, bullying from siblings, or insufficient milk for the mother.
Weak kids may need more food and warmth.
The symptoms can vary, but typically include weakness and lack of coordination in the legs, a limp tail, and a tendency to fall over or struggle to stand. In severe cases, the goat may be unable to stand or nurse, and it may show signs of lethargy, depression, and reduced appetite. This occurs in the first few hours after birth.
Diagnosis of weak kids is typically based on a combination of clinical signs and a physical examination, as well as a review of the goat’s history and management. Treatment of the animals may involve correcting any underlying causes, such as hypothermia or malnutrition, and providing supportive care, such as warmth, nutrition, and hydration. In severe cases, intravenous fluids and antibiotics may be necessary.
Weak Kid syndrome can be alleviated through proper management of newborn goats, including ensuring that they are kept warm and dry, providing adequate nutrition and hydration, and ensuring that they receive sufficient colostrum within the first few hours of life. It is also important to monitor for any signs of illness and to seek veterinary care promptly if any concerns arise.
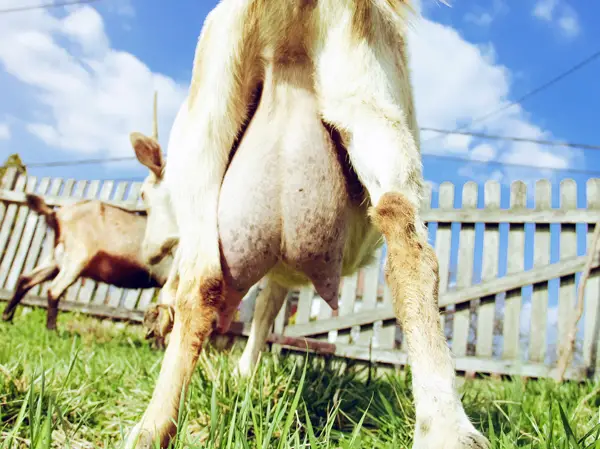
Goat Mastitis
Mastitis is an infection of the mammary glands in goats. It can cause swelling, pain, and decreased milk production. The udders can become swollen and painful.
Check out our thorough stand alone article on goat udder issues.

Goat Ketosis (Pregnancy Toxemia in Goats)
There is a good chance you have heard of the Keto Diet. You might even be eating this way, or know someone who is. For humans, being in ketosis may have benefits. In goats, it causes death.
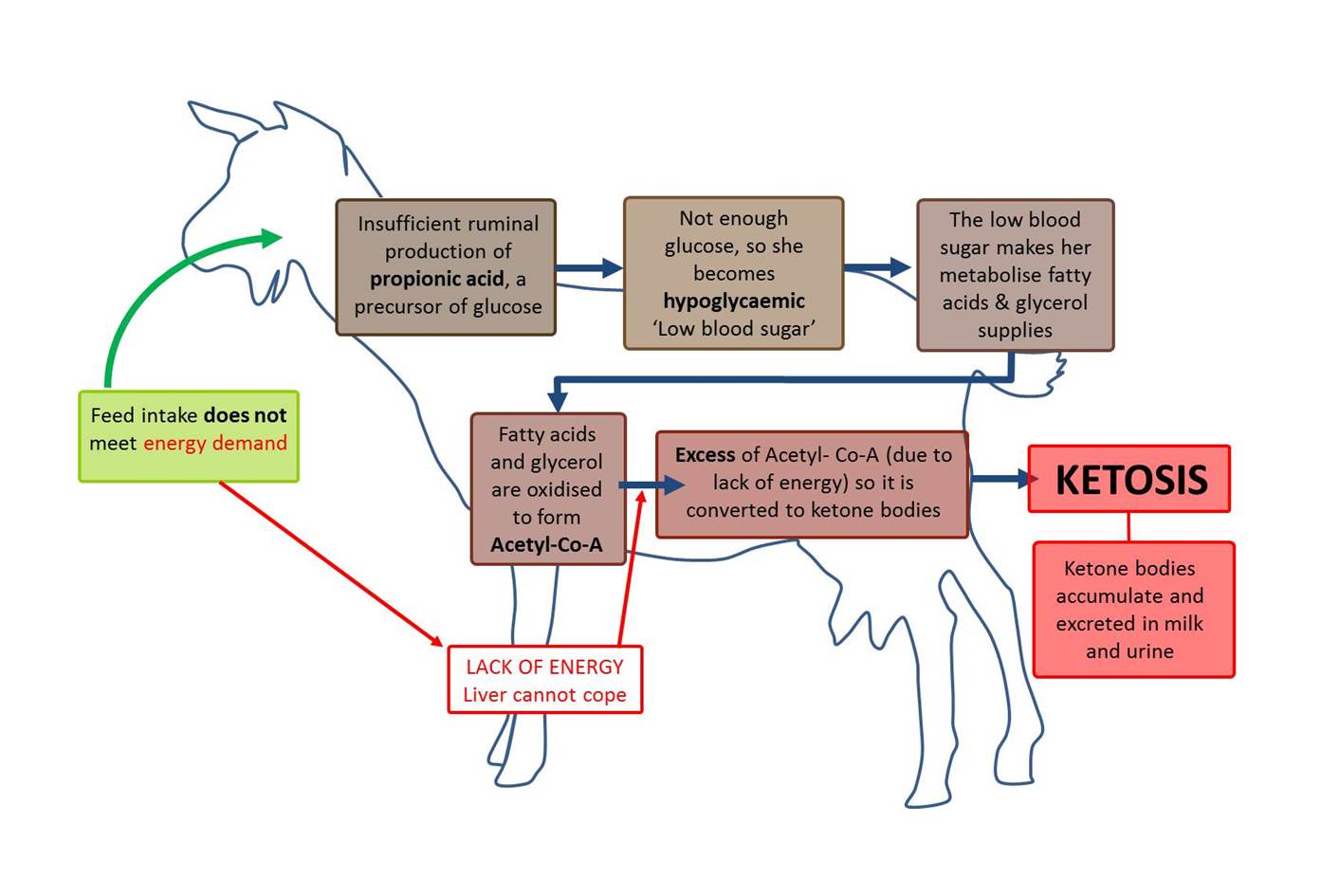
Goat ketosis, also known as pregnancy toxemia, is a metabolic disorder that affects pregnant goats and can occur when they are unable to meet the increased energy demands of pregnancy. This typically develops during the last 6 weeks of gestation in goats that are pregnant with more than one fetus. The condition is characterized by an excessive production of ketones, which are metabolic byproducts, and can result in symptoms such as weight loss, decreased appetite, and lethargy.
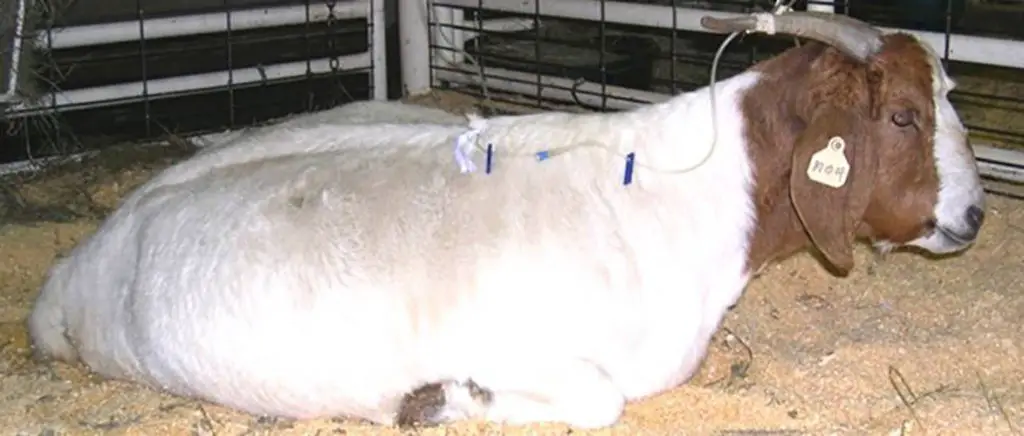
If the goat cannot eat enough of her normal diet to get glucose, then her body switches to burning fat. This creates ketones in her blood, which are toxic. Other factors that may contribute to the development of goat ketosis include stress, illness, and poor nutrition. If the goat is carrying multiple fetuses, there may not be enough room in her rumen for her to process enough food. If a pregnant goat is transported, even briefly, she is vulnerable because her nutrition intake is disrupted and the transport induces stress.
The symptoms of goat ketosis can vary, but typically include weight loss, decreased appetite, lethargy, teeth grinding, dull eyes, and a sweet or fruity odor on the breath, which is due to the presence of ketones. In severe cases, the goat may develop neurological symptoms, such as muscle tremors, seizures, stargazing, and recumbency, and it may go blind or be be unable to stand. Ketones can be detected in urine test strips. If your pregnant goat is behaving unusually or showing signs of distress, contact your vet immediately.
Your veterinarian may recommend that you treat goat ketosis by providing supplemental nutrition, such as glucose, molasses, or high-energy feeds, and administering propylene glycol. In severe cases, delivering the kids via C-section may be required. This can save the dam, but usually not the kids.
Prevention of goat ketosis can be achieved through proper management of pregnant goats, including ensuring that they receive adequate nutrition, avoiding stress, and monitoring their body condition closely. If you suspect that your goat has ketosis, it is important to consult a veterinarian promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Copper Toxicity in Goats
Copper toxicity, also known as copper poisoning, can occur in goats when they consume excessive amounts of copper. Copper is an essential nutrient that is required for normal growth and health in goats, but too much copper can be toxic and cause a variety of health problems.
The symptoms of copper toxicity in goats can vary, but typically include digestive disorders, such as anorexia, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, as well as liver and kidney damage. Copper accumulates in the liver. In severe cases, copper toxicity can result in liver failure and death.
The cause of copper toxicity in goats is usually due to the consumption of feed, water, or supplements that contains excessive amounts of copper. Animals being prepared for showing are especially vulnerable. Beware of feeds that contain high levels of copper, feeds that are formulated for other species that your goats might eat, the copper content of mineral supplements, and anthelmintics. The copper content of all these are cumulative in your goat’s liver.
Diagnosis of copper toxicity in goats is typically based on a combination of clinical signs, a physical examination, and laboratory tests, such as blood tests to measure the levels of copper in the blood. Animals often die within 2 days. Treatment of copper toxicity is not usually successful, and efforts should focus on prevention.
Prevention of copper toxicity in goats can be achieved through proper management, including ensuring that goats receive a balanced diet that meets their nutritional requirements, avoiding the use of feeds that contain excessive amounts of copper, being cautious with supplementation, and ensuring that goats don’t have access to feed meant for other animals. Work with you vet and local extension office to measure the mineral content of your forage pasture. If you suspect that your goat has copper toxicity, it is important to consult a veterinarian promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Thiamine Deficiency in Goats
Thiamine deficiency in goats is a nutritional disorder that affects goats and results from a lack of thiamine (also known as vitamin B1). Thiamine is an essential nutrient that is involved in many important functions in the body, including the metabolism of carbohydrates, the maintenance of nervous system function, and the production of energy. Goats do not absorb Vitamin B1 from feed. Instead, they create thiamine in their rumen.
Goat kids are particularly susceptible to thiamine deficiency as they wean off milk fed and begin eating grasses (and become ruminants), along with any situation that causes the goat to stop eating or a change to their diet.
When goats are deficient in thiamine they can get Goat Polio. Read more in the Goat Polio section above.

Tapeworms in Goats
Tapeworms are parasites that can infect goats and may cause a variety of health problems. Tapeworms belong to the class Cestoda and are commonly found in the small intestine of infected goats.
Tapeworms are just one of the different parasites that can live inside the goat.
Many goat parasites are invisible to the goat farmer, but infestation by the tapeworm is not. You will be able to see wriggle worm segments in the goat’s feces. It if for this reason that tapeworms are seen as a source of concern.
Tapeworm larvae live inside mites, and the goats ingest them when the inadvertently eat the mites when grazing.
Tapeworms grow inside the goats’ intestines, and do absorb nutrients from the goats.
There is debate, however, as to whether tapeworms actually cause harm to the goat, or whether their primary problem is inducing the “yuck” factor in the farmer. Parasites such as the barber pole worm and liver fluke are much more problematic.
If the infection is very heavy then it can lead to intestinal blockage. At that time there is a problem, and controlling it is in order. Before that however, Michigan State University Extension recommends that you learn to live with the parasite.

Paratuberculosis in Goats (Johne’s Disease in Goats)
Johne’s (Yo’-nees) disease is a serious and dangerous disease that is widespread, which can ultimately result in the death of your goat(s) as well as expensive and time consuming herd recovery procedures. The disease is found worldwide in goats, sheep, cattle, elk, bison, and deer. It is particularly common in dairy cattle.
Johne’s disease primarily impacts ruminants. Non ruminants that are omnivores or carnivores ( such as mice, pigs, wild rabbits, weasels, fox, raccoons, non-human primates, and birds) also get infected, but they may not get sick. According the Merck Veterinary Manual, and Eco Health, Johne’s disease may be related to the human disease, Crohn’s disease.
Johne’s disease in goats is the result of an infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). The bacterium is spread by animal feces, and it can survive in pastures for longer than 1 year. Goats likely ingest paratuberculosis (MAP) when they eat contaminated feed or drink contaminated water. They may also get it when nursing on contaminated teats or from consuming milk.
There is no cure for Johne’s disease, and in goats, the only visible sign may be emaciation, which results in death. The emaciation does not occur, however, until years after infection, and during that time the infected animal has been spreading the bacteria through its feces.
There are 4 stages of Johne’s disease:
Stage 1
The first stage usually occurs in goats under 2 years old. The goat becomes infected, but the the infection cannot be detected by any current testing methods.
Stage 2
In the second stage, the animals seem healthy, and their blood tests show no infection. They being to shed the MAP bacteria in their feces, however, and the bacterium is detectable.
Stage 3
In the third stage, the animal begins to show symptoms of illness, particularly when it is stressed. The goats may lose weight even though they are eating, and have decreased milk production. At this stage, cattle will have diarrhea, but this is not typical for goats. Once the stress has subsided, the animals will stop showing symptoms. The feces are shedding billions of bacteria in this stage.
Stage 4
This is the final and fatal stage. The animals are emaciated, even though they continue to eat. For goats, this may be the first visible symptom of the disease.

Herd Management
If you find one goat with Johne’s disease, there is a good chance that many other goats have it. You must contact your veterinarian. You will then have to begin herd management, which includes testing and culling your herd.
You can recover your herd, but it is takes years and is expensive.
Prevention
Prevention is the most cost-effective way to manage Johne’s Disease.
You must take control of your herd, and be extremely selective about new animals that are introduced to your herd. You should test your herd at least annually and only accept new goats from farms that show you negative laboratory tests. Buy adult goats that have a long history of negative tests, and only buy from a small number of herds. Ensure that the nannies of all kids you buy test negative.
University of Wisconsin Resource
A full list of steps that you should take to prevent Johne’s disease can be found here. This is just one page from the University of Wisconsin’s website about Johnes’s Disease, Johnes.org.
This disease is not to be taken lightly, and if you are a goat farmer, you are encouraged to read the entire johnes.org site thoroughly.
Protect Your Herd
For dairy and meat cows, there may be state and national laws that require testing and reporting to limit the spread of Johne’s disease. Goats, however, fall into the category of “agriculture animals” and so there are not usually specific testing requirements.
As a result, you must take the responsibility for doing what you can to protect your herd.
Video: Carolina Kiko Classic – Johne’s Disease in Goats
Here is a video from the the Carolina Kiko Classic meat goat conference. This is a full length class taught by Fred Brown, DVM, on Johne’s disease in goats. The whole video is worth watching. Skip to 30:37 to find out the best time to test your goats.
Listeriosis in Goats
Listeriosis is a bacterial disease caused by the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. It can affect goats, as well as other animals and humans. Listeriosis can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, depending on the species and the individual’s immune status.
In goats, listeriosis can cause blood poisoning and abortion. However, listeriosis usually causes encephalitis, which means the brain becomes inflamed. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including fever, muscle stiffness, mastitis, circling in one direction, loss of coordination, depression, and red tissues around the eyes. The goat may salivate continuously, and have facial paralysis on one side. The disease can also cause central nervous system symptoms, such as tremors, seizures, and depression. In severe cases, listeriosis can lead to death.
The cause of listeriosis in goats is usually due to the consumption of food or water contaminated with L. monocytogenes. They can get the bacteria in their eyes, inhale it, or swallow it. The bacteria are common in soil, and it also found in hay bales that have started to rot, silage that has not fermented properly, manure, and dirty feed bunks.
Prevention of listeriosis in goats can be achieved through proper management, including isolation of infected animals, disinfection of floors, pens, feed bunks, and water troughs. Practice good hygiene and sanitation practices.
Infected goats do not usually recover unless caught early enough. Aggressive treatment with antibiotics sometimes will save your goat’s life.
If you suspect that your goat has listeriosis, it is important to contact your veterinarian promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
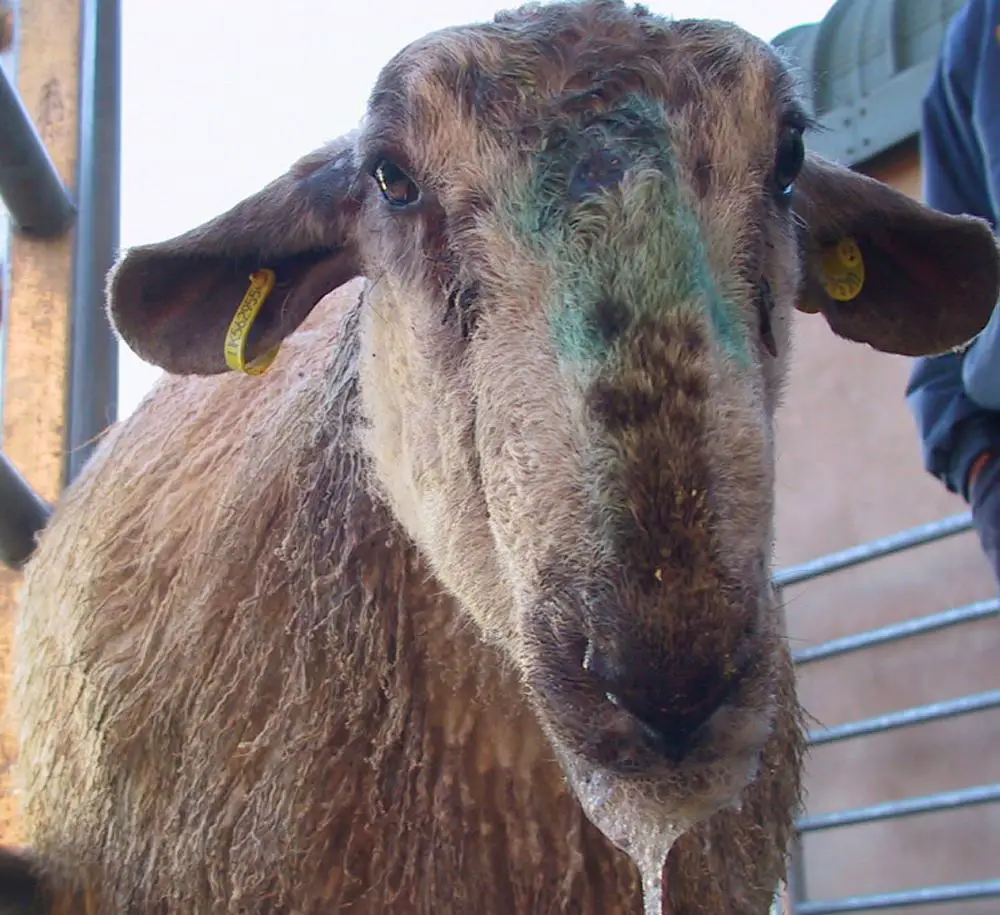

Photo Credits
- Vetvoice.com.au
- Washington State University Extension
- Kevin Washburn, DVM in MSD Vet Manual
- Thrifty Homesteader website
- Video made by Azad Jain
- NSW Australia Local Land Services
- Backyard Goats .I am Countryside website
- Farm Health Online
- Paratuberculosis Association
- Dr John Prescott in Merck Veterinary Manual
- Oklahoma State University
- Morning Chores Website




